Top 5G Network Security Issues in 2028 – 5G OWASP for Networks
Two weeks ago in our 5G security projections for the future article, we introduced 5G security on a high level as an evolution of the 5G – The security of things to come. Now we want to jump forward in time to look specifically at what the top 5G network security issues may be in 2028.
We at AdaptiveMobile Security have a wide and deep experience of past and current threat landscape, so let’s start from there and make a prediction of what might be the most common security issues in 2028. The better we understand the potential issues right now, the better we can counter them in the future and be ready when we see those life issues.
5G in the year 2028
Imagine yourself in 2028: 5G is deployed in all major cities, there are still some rural areas which just run LTE. 5G is used not only in the radio access network but also in the core of your home operator and the countries you travel to.
Eight years have passed after COVID19 waves, virtual and online strategies are still widely used. There are a lot of small local networks e.g. your employer, your shopping mall and service providers, which provide enhanced connectivity and applications. You might even buy a nice house a bit away from the city, as you no longer have to commute every day.

Figure 1: Man working from country house terrace using 5G connection.
Entertainment, hospitality services, manufacturing and production sites, health service, city services, traffic management, and logistics, all have taken the opportunity offered by connecting their systems using 5G technology. Maybe even, some companies have turned their offices fully virtual in 2028.
The introduction of generic 5G application programming interfaces (APIs) provided the “key” to allow easy integration of very different systems with each other locally and worldwide using the roaming network to enable many different applications.
This easy integration with the tools available has not been done unobserved or has not been already penetrated by many hackers… There have been some targeted attacks in 2027 on those APIs that were possible due to neglected security configurations, which resulted in a wide-spread ransomware attack.
The GSMA Association and OWASP
The GSMA Association, where most of the operators and telecommunication service providers of the world are represented, has evolved its vulnerability exposure program to cover service API interface security towards industrial players. The OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) is well known for its mission to improve the security of software and its yearly publication of the most common software vulnerabilities.
In our envisioned future in 2026 the OWASP will have founded a special subchapter for mobile core network connected API vulnerabilities and attacks as they would have suffered from similar, but not identical problems than Internet web APIs software.
This year in 2028, they published their first joint report on 5G OWASP Top 10, which is the telecommunication counterpart for the famous web API OWASP Top 10.
Top 5G network security issues of 2028
We have also created a top 10 that we are going to split into two parts. The first part explores the top 5 core network-related 5G security issues of 2028 that we at AdaptiveMobile Security envision:
1.Lack of Input Parameter Validation
The 5G REST API’s Information Elements (IE) are often nested or multipart and of different data types and sizes. This poses the risk that an attacker can put an IE into an IE, or in general terms, put untrusted data into the API as part of the query (remember the good old SQL injection or a beautiful buffer overflow attacks). The receiving interpreter in a core telecommunication network would parse the information and might give an attacker unauthorized access to information or executing unauthorized actions. Therefore, for proper input sanitization, it is essential to:
- Validate length, data type and data format on the information element level
- Validate nesting depth, occurrence and structure of the IEs
- Cross validate the information with existing subscription and network node related information e.g. identity ranges, IP addresses, etc.
- Define appropriate size limits and frequency for the whole API call
Even if in 2028 the core networks and interconnection would support 5G, there are still some networks or parts of the network that work with legacy protocols. Therefore, the nodes that support interworking need to filter and analyze traffic from the legacy generations, which have also proprietary extensions and nested elements.
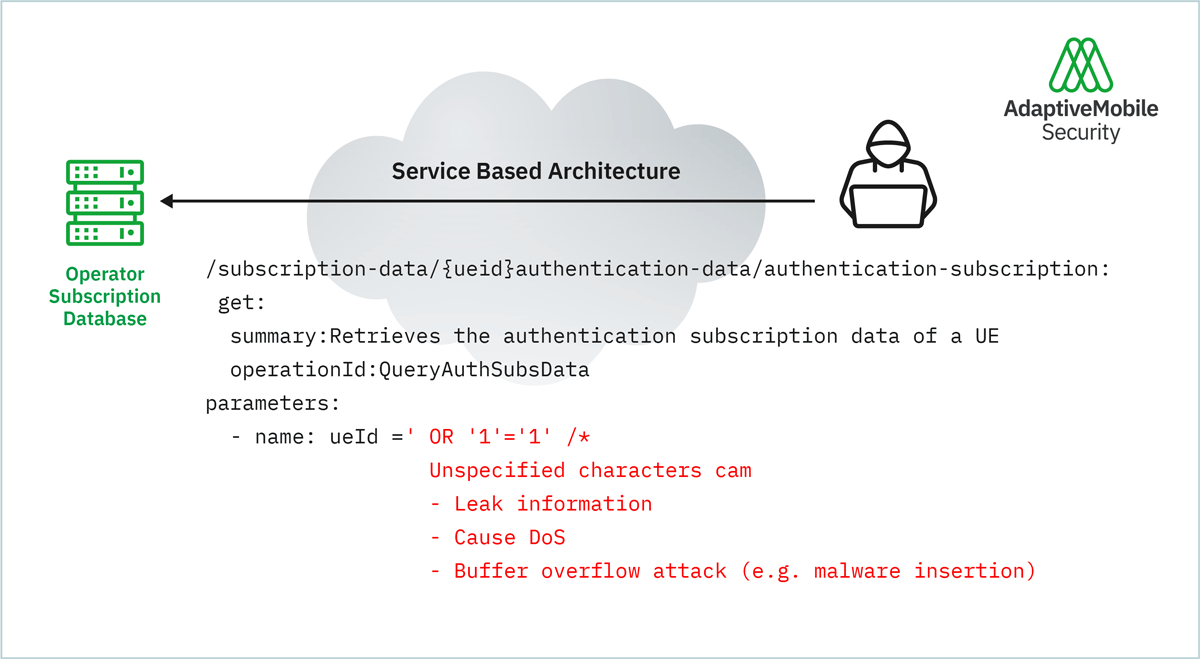
Figure 2: Example – Lack of input parameter validation attack
2. Broken Communication Partner Access Control
5G core networks use OAuth in the Network Repository Function (NRF) as specified in 3GPP TS 33.501 specification to authorize REST API requests to the core network nodes on the Service Based Architecture (SBA). OAuth is a very commonly used Internet protocol for authorization.
But 5G is much more complex than 3G or 4G and there are thousands of Information Elements (IE) in 5G and every new release of the specifications brings new ones and each operator has a wide range of partners and contracts.
The year 2028 second Top 10 was that the authorization on information element level was often not sufficiently fine-grained and did not correspond to the actual contract between operators and service providers. Common access or modification rights were granted to a larger than required IE set. One root problem was the common usage of wildcards for access control when using the REST API, which allowed attackers to launch attacks, ransomware attacks being the most common ones.
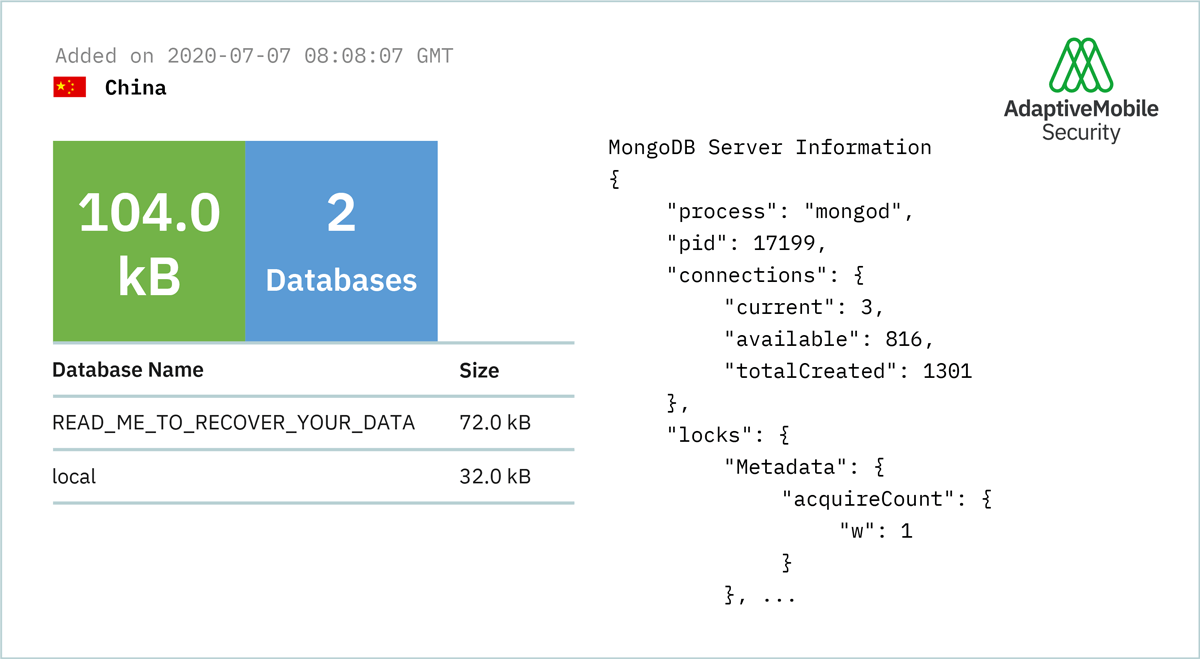
Figure 3: Ransomware attack on operator database in 2020
Usage of standard contracts with associated standard authorization templates which reflect the contractual arrangements could lighten the configuration burden. In addition, monitoring and traffic analysis can reveal unauthorized access and information extraction. Which brings up the next important issue and our number 3:
3.Insufficient Logging and Monitoring
Insufficient logging and lack of monitoring, coupled with missing or ineffective integration with incident analysis, response and filtering updates, allowed attackers to further attack systems that lie behind the firewall. The attackers maintained persistence, made lateral movements through the network and were able to send messages on behalf of the compromised network operators, extract, and in some cases destroy data.
The average time for the data breach discovery for telecommunication core network attacks in 2028 was 189 days (this seems to be a fair guess looking at the breach discovery time large IT companies have today). The breaches were commonly discovered when roaming partners that monitored their attacks and traffic complained about undesired traffic and questioned the originating operator about what was happening.
In some cases, local governments imposed heavy fines for the large data breaches due to lack of suitable filtering and monitoring.
4.Sensitive Data Exposure during Transit
The Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) has specified 4G Interconnection security between operators for signalling traffic, the adoption strategies and technology type of adoption vary, in some cases, one may see hop-by-hop TLS deployments or other routing approaches that offer value-added services provided by intermediate nodes.
Those routing paths sometimes lead through less trusted networks or routes and cause unintentional data exposure. The exact extent of data exposure is not known. Some high-profile national security related cases became known in 2028 due to triggering messaging filters for fraudulent activities.
5.Broken Authentication
TLS certificates and related keys were compromised without the owner realizing it and they are even for sale. The usage of outdated revocation information delayed the blocking of the TLS sessions using the stolen certificates. This then resulted in missing or inadequate authentication and resulted in the theft of 5G JSON web tokens, API access tokens or similar authentication information.
Unauthorized access to API was obtained, as some operators relied on authentication only and not on the additional authorization. Up-to-date revocation information in case of compromise helps to contain the damage caused by such a compromise. The best approach for a timely revocation approach for interconnection security is still under discussion and delayed due to trust questions.
Read now the third in a series of three 5G network security projections: OWASP: Top 5G Vertical Industry Security Risks in 2028.






